Factors Affecting Equilibria
Factors Affecting Equilibria: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Factors Affecting Equilibrium, Le Chatelier's Principle, Effect of Pressure Change on Equilibrium, Effect of Concentration Change on Equilibrium, and Effect of Inert Gas on Equilibrium.
Important Questions on Factors Affecting Equilibria
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
At a fixed temperature, the volume of the reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant and degree of dissociation ?
For the chemical reaction , the amount of at equilibrium is affected by –
In which of the following equilibrium, change in the volume of the system does not alter the number of moles –
The exothermic formation of is represented by the reaction
Which of the following will increase the quantity of in an equilibrium mixture of and
The reaction is exothermic and reversible. A mixture of and is at equilibrium in a closed container. When a certain quantity of extra is introduced into the container, while keeping the volume constant, then which statement among the following is true?
At the equilibrium of the reaction, , the number of moles of at equilibrium is affected by the
Which of the following reactions will not get affected on increasing the pressure?
Consider the following reaction in closed container at equilibrium. What would be the effect of addition of on the equilibrium concentration of ?
At the equilibrium of the reaction, , the number of moles of at equilibrium is affected by the
What would happen to a reversible dissociation reaction at equilibrium when an inert gas is added while the pressure remains unchanged? Here
The reaction is in equilibrium. Now the reaction mixture is compressed to half the volume
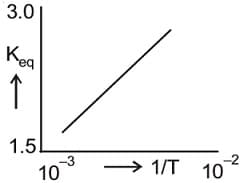
From the following graph represents:
By adding inert gas at a constant volume, which of the following equilibrium will not be affected?
For the equilibrium:
What will be the concentration of , if the equilibrium concentration of is doubled?
Which of the following statements is incorrect with respect to the given spontaneous reaction?
The ionisation constant of in water is at . The rate constant for the reaction of and to form and at is . If dissociation constant of water at is . If of water at is then the heat of neutralisation is:
For the reaction given, , the forward reaction at constant temperature is favoured by
In the given diagram, a cylinder is divided by partition . In compartment two gases and are in equilibrium with each other.
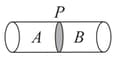
The reversible reaction
is at equilibrium. What would not happen if ammonia is added –
Dissociation of phosphorus pentachloride is favoured by –
